Lucid v4 now supports the creation, deployment, maintenance and playing of interactive pathway keys (also often called dichotomous keys). Pathway keys are one of two main types of identification keys. The other type, matrix keys (also often called interactive or random-access keys) are also supported by Lucid.
A pathway key is a traditional form of identification guide that takes the form of a series of questions or statements, each question or statement leading to either another question or statement, or to a result (an identified taxon or entity). Pathway keys are so named because the questions or statements are arranged in the form of a branching pathway, each branch ultimately leading to an identification. At each branching point a question with two or more answers, or two or more statements, are presented. The answer or statement that best describes the entity (taxon or other thing) being identified is chosen at each step.
There are several traditional ways of writing pathway keys, but all have the same basic structure.
An example of a simple couplet statement key.
Statements are written in groups (couplets), each with a go-to. Choose which statement of the couplet is correct for the specimen to be identified, then go to the couplet number indicated.
1. Flowers blue……………………………2
1a. Flowers red…………………………….3
2. Fruits fleshy………………..Species 1
2a. Fruits woody……………….Species 2
3. Trees…………………………..Species 3
3a. Shrubs……………………………………4
4. Leaves hairy………………..Species 4
4a. Leaves not hairy………….Species 5
The same key written as a simple indented statement key
Statements in a group (couplets) have the same indent level. Choose which statement of the couplet is correct for the specimen to be identified, then go to the couplet immediately below
Flowers blue
Fruits fleshy…………………..Species 1
Fruits woody………………….Species 2
Flowers red
Trees…………………………….Species 3
Shrubs
Leaves hairy………………..Species 4
Leaves not hairy…………..Species 5
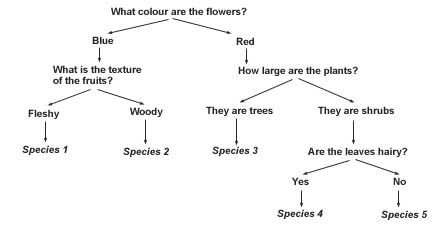
The same key written as a branching tree with questions and answers
Begin at the top of the key with the first question, choose which answer is correct for the specimen to be identified, then follow the arrow to the next question.
Next – Starting a pathway key

